Architectural Energetics
CATEGORY: Architecture (Research)
DURATION: 3 months
DESCRIPTION:
Over the past two centuries, the development of modern society has been supported by the use of natural resources at a rate much faster than can be sustained. The 21st century must be defined by a symbiosis between architecture and nature in the use of global material and energy flows. In nature, species develop complexity, diversity and hierarchy to maximize greater amounts of incoming solar energy. They dissipate this energy for production and reproduction while also contributing to feedback processes that help increase the total dissipation of the larger ecosystem. More sustainable patterns of building must be based on similar principles of metabolism if we are to enjoy healthier, more vibrant and abundant ways of living in this century.

Laws of Nature
Nature tends to follows certain laws of energy and hierarchy, mainly:
1. Energy quantity (i.e. energy cannot be created nor destroyed, also known as the Conservation Law).
2. Energy quality (i.e. although conserved, energy degrades over time, also known as the Entropy Law).
MATERIAL AND ENERGY CYCLES
The organization of systems depends on material and energy flows. Materials are coupled with the transformation of energy (e.g. solar energy + carbon + water + soil nutrients = tree).
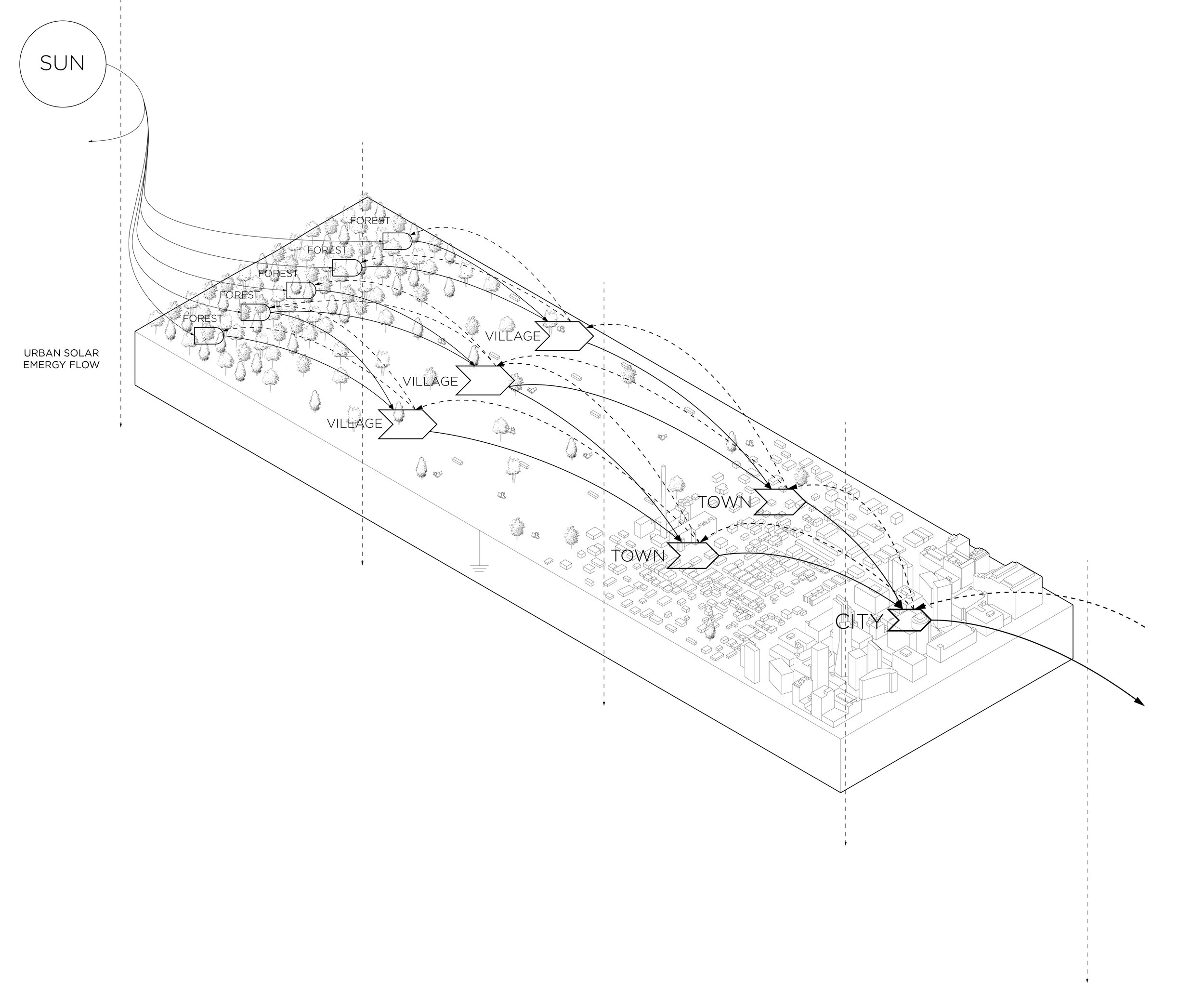
EMERGY FLOW
Although different forms of energy do different qualities of work, all energy can be converted to a single unit that expresses all the direct and indirect processed needed to make that specific form of energy. Since almost all energy on earth comes from the sun, a common unit of measure can be used to trace that energy back to its original source, known as emergy. Spelled with an “m” to indicate the energy’s “memory,” it us expressed in solar emjoules (sej), therefore, defining all energy flows in an energy system.
FEEDBACK REINFORCEMENT
Downstream elements feed back high-quality materials and services to upstream elements reinforcing the processes that contribute.
PULSING
All systems tend to move away from steady state over time. They grow to a maximum high-diversity state but then are followed by a process of removal and regrowth.
ARCHITECTURE AS CONCENTRATED ENERGY
The second law of energy states that structures of higher concentration than their environment tend to disperse and depreciate over time. Concentrating structures, therefore, requires available energy to do concentrating work.
As available energy works to concentrate material, much of the energy becomes degraded (to heat, material recycling, etc. losing its ability to do further high quality work) while emergy still increases. The mass/emergy ratio of the concentrated material increases along the energy hierarchy, implying the energy role of materials in the building process.
Self-organizing systems tend to spatially converge materials towards centers. The greater the convergence, the more emergy is required per unit weight and the less material can be used, making higher concentration areas more scarce, but of higher quality.

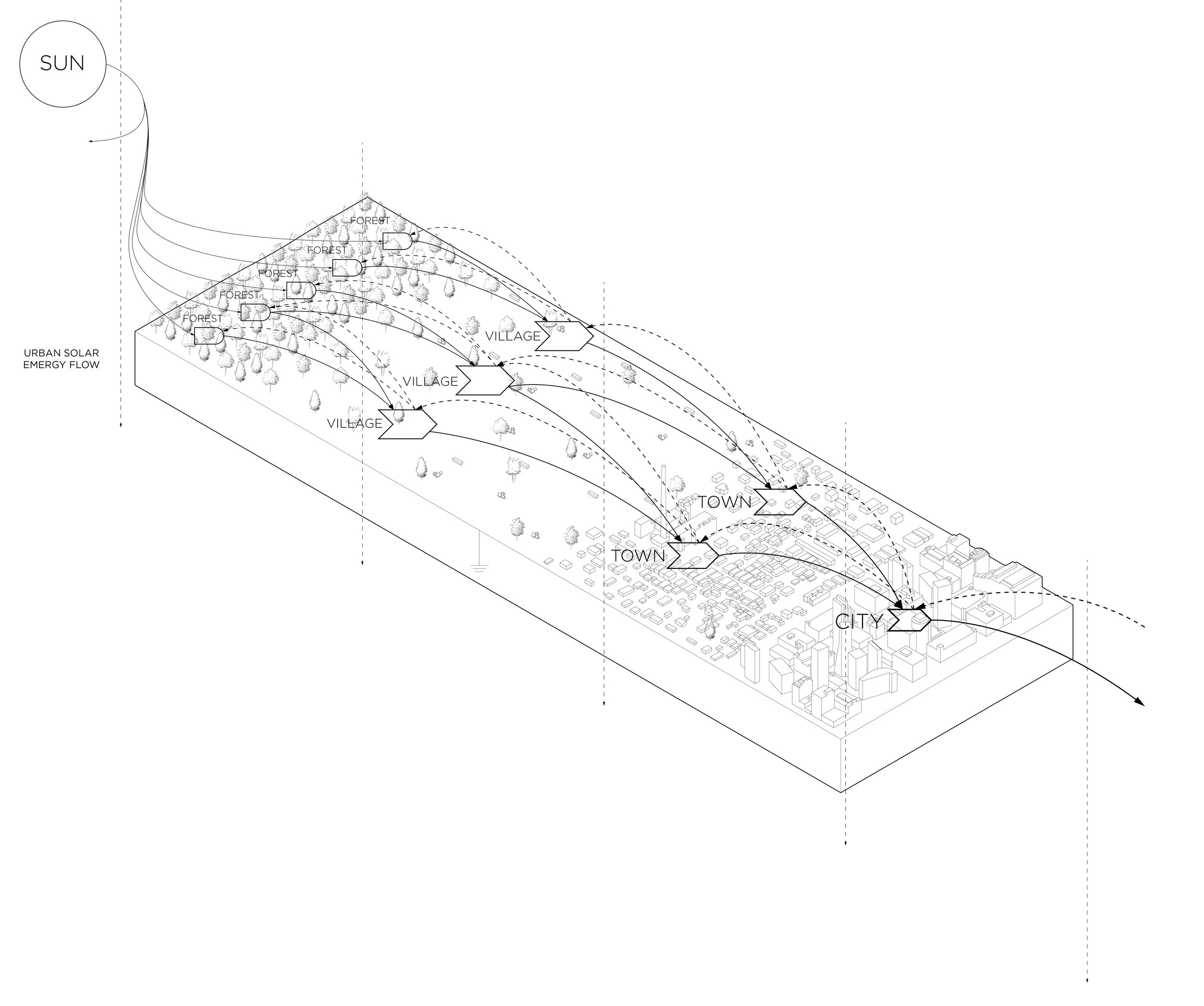
Energy Hierarchy
Energy flowing in a system builds units of structure and processing. At each step in the process, the quality of the transformed energy increases. A joule of lumber is of higher quality than a joule of the original tree trunk. lt is more concentrated and more usable in building. Similarly, a city contains greater concentrations of energy than a town of the same size, a town more than a village, and a village more than the surrounding forest.

Buildings as Thermodynamic Engines
An architecture based on thermodynamics has the potential to transform building design from a subjective art-form to a predictive science.
PRINCIPLES
1) Buildings and cities are (always and only) open systems. A building’s system boundary extends beyond its exterior skin just the same way a city’s system boundary extends beyond the urban core. Buildings and cities exchange energy and material with their environments.
2) Buildings must maximize and reinforce natural energy and material flows. Natural processes must serve as many building functions as possible (e.g. lighting, heating, cooling, ventilation, waste management, etc). It is therefore essential to use renewable and local materials.
3) Buildings must be designed for and built by their local contexts (social, environmental, historical, etc).
4) Buildings must pulse with their local environment. Organisms avoid decay by continuously processing matter and energy.
5) Buildings must be part of an ecosystem of circulating energy and material. Building components designed for assembly and disassembly allow for maintenance, repair, and high quality feedback over their life-cycle.
TRANSFORMITY AND ENERGY QUALITY
As energy flows and gets transformed through a system, the amount of available energy decreases, while the quality of that energy increases. While downstream energy sources contain less available energy (second law), their emergy stays the same (first law). This emergy/energy ratio is defined as transformity.
INFLUENCES AND PRECEDENTS
The work of Howard T. Odum on systems ecology and its translation to architecture and design by Kiel Moe provided much of the theoretical foundation for this project. Research and architecural precedent projects from Le Corbusier, Walter Gropius, Buckminster Fuller, Kieren Timberlake, Alejandro Aravena, and others helped develop much of the thinking for establishing more symbiotic relationships among design, industrial manufacturing, building construction, and ecology.
